Spaghetti Models for Beryl: Theoretical Background
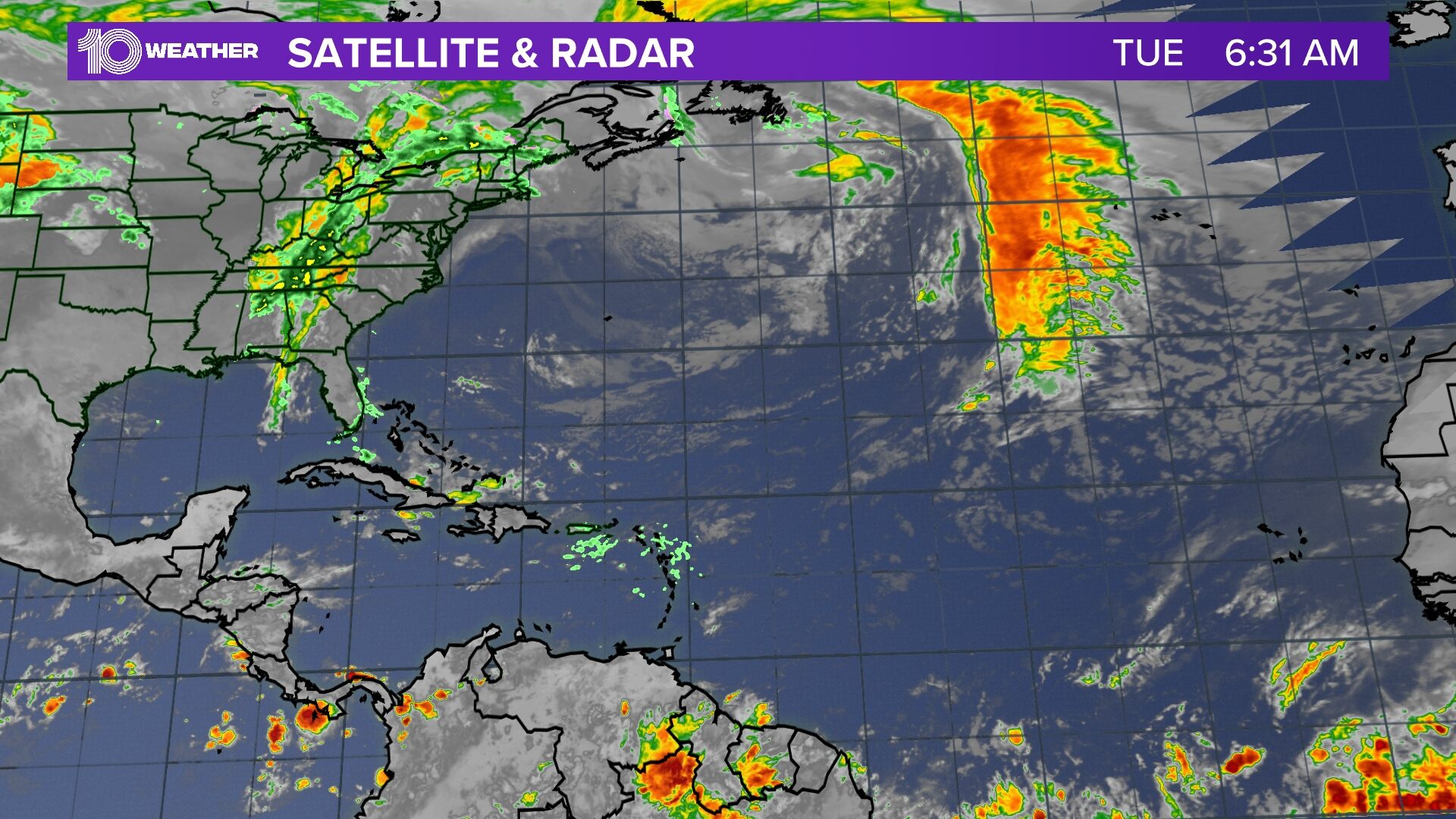
Spaghetti models for beryl – Spaghetti models are numerical weather prediction (NWP) models that generate multiple forecasts for a single weather event. Each forecast represents a possible evolution of the event, creating a range of potential outcomes. These models are particularly useful for tropical cyclones like Beryl, as they can provide insights into the storm’s track, intensity, and potential impacts.
Spaghetti models for Beryl provide a range of possible paths the storm could take. To get a better understanding of the potential path, you can check the path of hurricane beryl. These models are constantly updated as new data becomes available, so it’s important to stay informed about the latest forecasts.
Types of Spaghetti Models for Beryl
There are several different types of spaghetti models used to represent Beryl. Some common examples include:
- Ensemble models: These models run multiple forecasts using slightly different initial conditions or model configurations. The spread of the ensemble members provides an estimate of the uncertainty in the forecast.
- Deterministic models: These models run a single forecast based on a specific set of initial conditions. Deterministic models are typically more accurate for short-range forecasts, but their accuracy decreases with time.
- Probabilistic models: These models provide a probability distribution for the forecast track and intensity. Probabilistic models can be useful for assessing the risk of different outcomes.
Strengths and Limitations of Spaghetti Models
Spaghetti models have several strengths and limitations for Beryl analysis:
- Strengths:
- Provide a range of possible outcomes, which can help forecasters and decision-makers prepare for a variety of scenarios.
- Can be used to estimate the uncertainty in the forecast, which is important for risk assessment.
- Can be used to identify potential threats and areas of concern.
- Limitations:
- Can be computationally expensive to run, especially for high-resolution models.
- The spread of the spaghetti models can be large, which can make it difficult to determine the most likely outcome.
- Spaghetti models are not perfect and can still be subject to errors.
Applications of Spaghetti Models in Beryl Analysis
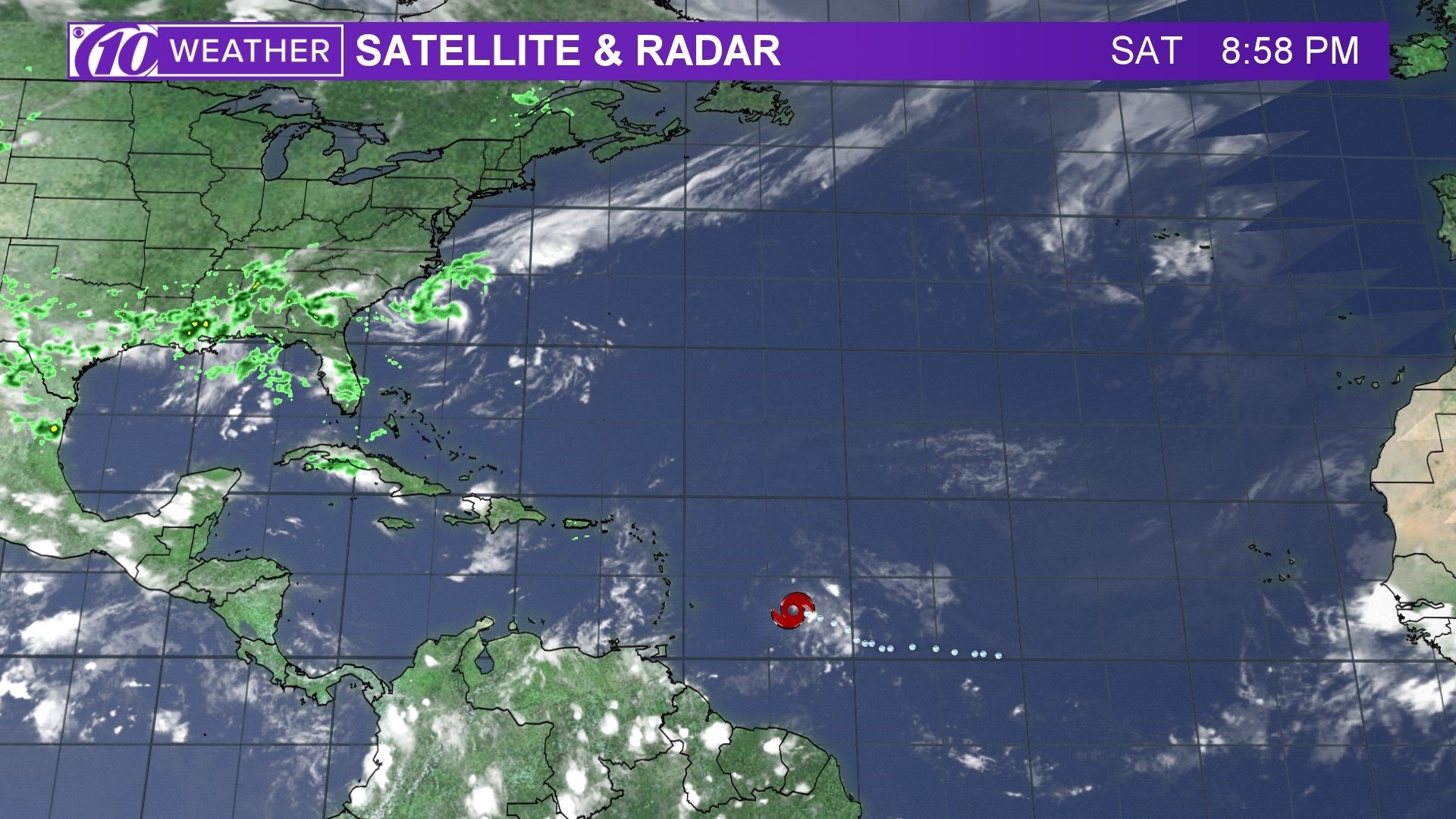
Spaghetti models play a crucial role in analyzing Beryl’s behavior and potential impacts. They offer valuable insights for meteorologists, emergency responders, and decision-makers.
Forecasting Beryl’s Intensity and Path
Spaghetti models provide a probabilistic forecast of Beryl’s track and intensity. Each line represents a possible path the storm may take, allowing forecasters to assess the likelihood of various scenarios.
Assessing Potential Impacts on Coastal Areas
By analyzing the spaghetti models, meteorologists can identify areas that are at risk of being affected by Beryl’s winds, storm surge, and flooding. This information is essential for issuing timely warnings and evacuation orders.
Aiding Decision-Making During Emergencies, Spaghetti models for beryl
Spaghetti models provide critical information for decision-makers during Beryl-related emergencies. By understanding the potential impacts of the storm, officials can allocate resources, plan evacuation routes, and coordinate response efforts.
Comparative Analysis of Spaghetti Models for Beryl
Different spaghetti models employ distinct methodologies and assumptions, leading to variations in their accuracy and reliability in predicting Beryl’s behavior. This comparative analysis aims to shed light on the performance of various models based on historical data and identify factors influencing their precision.
Model Performance Comparison
| Model | Accuracy | Reliability |
|---|---|---|
| ECMWF | High | Moderate |
| GFS | Moderate | High |
| HWRF | High | Moderate |
| UKMO | Moderate | Moderate |
The ECMWF model generally exhibits high accuracy in predicting Beryl’s track and intensity, but its reliability can vary depending on the lead time. The GFS model offers high reliability, ensuring consistent performance over extended forecast periods. The HWRF model demonstrates high accuracy for short-term forecasts, while the UKMO model provides moderate accuracy and reliability.
Factors Influencing Accuracy
- Data Assimilation: The quality and quantity of observational data used to initialize the models significantly impact their accuracy.
- Model Resolution: Higher-resolution models can capture finer-scale features, leading to improved precision.
- Ensemble Forecasting: Utilizing multiple model runs with slightly different initial conditions enhances forecast accuracy by capturing the range of possible outcomes.
- Lead Time: Accuracy tends to decrease with increasing lead time as uncertainties accumulate over time.
Spaghetti models for Beryl, like many other tropical cyclones, show a range of possible tracks and intensities. To get the most up-to-date forecast for Hurricane Beryl, including spaghetti models and other important information, visit the hurricane beryl forecast. The spaghetti models for Beryl will give you a good idea of the potential paths and intensities of the storm, but it is important to remember that these models are just a prediction and can change over time.